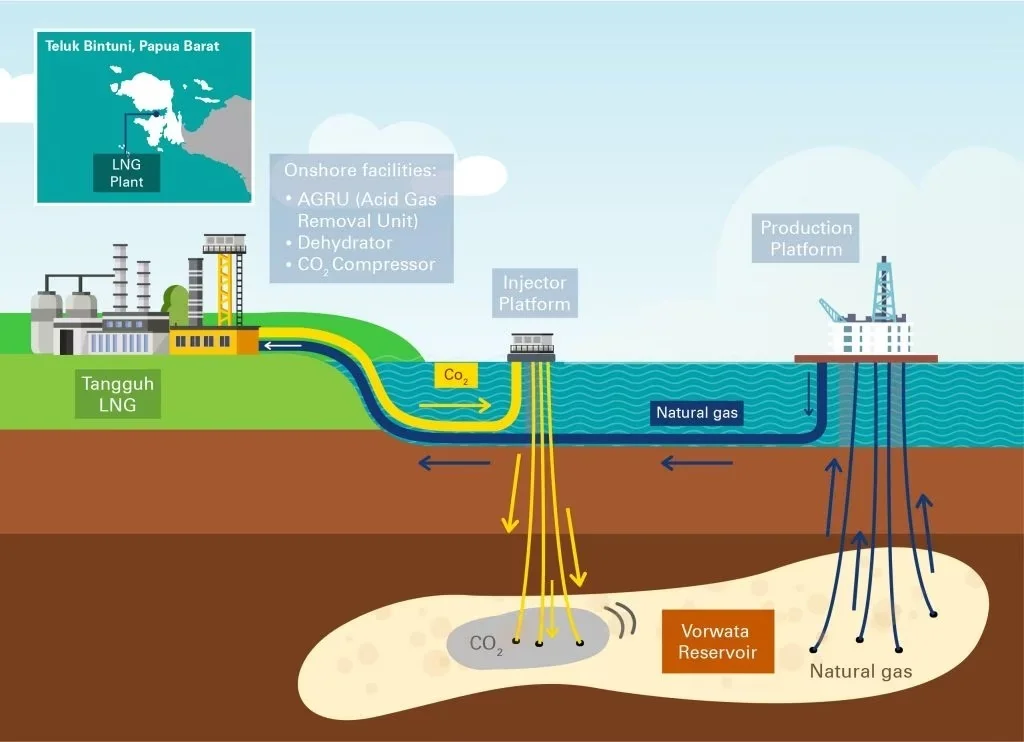
Indonesia Combines Bioenergy and CCS to Combat Climate Change
Indonesia is advancing its climate action strategy by integrating bioenergy production with Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) technology. This innovative approach, known as Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS), is expected to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions while addressing the nation’s growing energy demands.
During a panel discussion at the COP29 UNFCCC conference in Baku, Azerbaijan, Ristianto Pribadi, Director of Forest Products Processing and Marketing at Indonesia’s Ministry of Forestry, highlighted the importance of BECCS. “With BECCS, we create a carbon-negative process to produce energy while simultaneously capturing carbon dioxide emissions,” Ristianto explained.
The BECCS initiative is a holistic strategy combining sustainable forest management with bioenergy production and carbon capture technology. Forest management ensures a consistent supply of biomass for bioenergy production, while CCS technology captures and stores the emissions generated. This integration creates a closed-loop system, reducing the environmental impact of energy production.
Indonesia’s commitment to BECCS innovation is supported by strong collaboration between government entities, private companies, and local communities. For instance, Marubeni Indonesia and PT Pertamina have signed a Joint Study Agreement (JSA) to develop BECCS projects. Marubeni’s industrial forest operations in South Sumatra not only produce biomass for energy but also neutralize carbon emissions through sustainable forestry practices.
As part of this initiative, carbon emissions from PT TEL’s biomass processing will be captured and stored in decommissioned oil wells managed by Pertamina. These wells, located only five kilometers from the forestry site, exemplify Indonesia’s unique advantage of having carbon storage facilities near biomass production areas. This reduces logistical challenges and enhances the project’s efficiency.
Senior Vice President Oki Muraza of Pertamina stated that the stored carbon dioxide could also enhance oil production or act as a fertilizer through photosynthesis. This dual-purpose utilization demonstrates the potential economic and environmental benefits of BECCS.
Despite its promise, the BECCS project faces challenges. High costs, infrastructure demands, and the need for advanced technology present significant hurdles. Additionally, strong partnerships between stakeholders are essential to ensure successful implementation and scalability.
Globally, Indonesia’s ambition to develop CCS technologies aligns with its broader climate commitments. With a potential storage capacity exceeding 400 gigatonnes of CO2, Indonesia is positioning itself as a regional hub for carbon management. As part of this effort, the government has introduced regulations to attract foreign investment in CCS operations, allowing up to 30% of storage capacity for imported carbon dioxide.
By combining innovative technology with natural resource management, Indonesia’s BECCS initiative not only addresses local environmental challenges but also contributes to global climate action. This pioneering approach showcases how developing nations can lead in sustainable energy solutions.
Read More






 Wednesday, 25-02-26
Wednesday, 25-02-26